Water can dissolve and absorb molecules from different substances, making it a universal solvent. Then, the dissolved particles in the water volume are referred to as Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) levels.
Once you understand the TDS level of water and which TDS is present, you can have a clear picture of the water’s overall quality.
If it is your first time hearing about TDS, you may find it confusing or wonder if it is really necessary. Keep reading and discover what TDS in water is and the reasons why you should measure it.
What is TDS?
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refers to the amount of organic and inorganic materials, including ions, salts, minerals, and metals, dissolved in a specific water volume. They essentially measure anything present in the water, which is not water molecules.
As a solvent, once water encounters soluble materials, the particles of those materials are absorbed into the water. Then, TDS are created.
Total Dissolved Solids in water come from anywhere, such as household plumbing systems, runoff from yards or roads, chemicals used for treating municipal water supplies, and natural water springs.
What is TDS Meter?
With a TDS meter, you can determine the Total Dissolved Solids in water. This small hand-held device measures the solution’s conductivity and then estimates the TDS from that reading.

Using a TDS meter is even more helpful since minerals, salts, and other dissolved ionizers increase the solution’s conductivity.
How is TDS Measured?
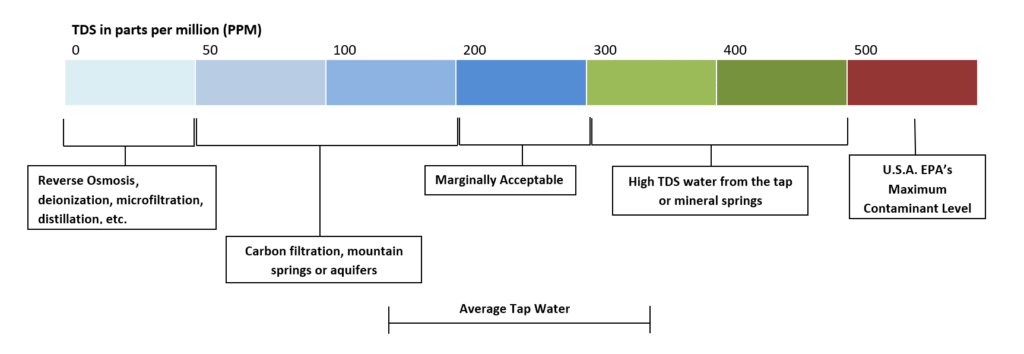
TDS is measured as water volume using milligrams per liter (mg/L) or parts per million (ppm). According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the recommended maximum TDS amount for drinking water is 500ppm.
If you use a reverse osmosis (RO) system, you can use the formula below to calculate the TDS percent rejection and measure the performance of the RO system:
Measure the raw feed water’s TDS through tester probes’ submersion into the tap water glass. Ensure to record the results.
Measure the RO water’s TDS by filling a glass with RO water. Then, submerge the tester probes into the water. Ensure to record the results.
You can calculate the percent rejection using the formula below:
% Rejection = Tap TDS – RO TDSTap TDS x 100
For example, the Tap TDS is 260ppm RO, so:
TDS = 20ppm Rejection = [(260-20260)] x 100 = [240260] x 100 = (0.923) x 100 = 92.3
Note that if the membrane has been replaced or the RO system is new, testing the RO water’s first tank is not advisable. The first tank may contain carbon fines or sanitizer that leads to a false reading.
Check out this video to have a bigger picture.
Why Should You Measure TDS?
Measuring TDS levels in water are the most effective way to know and understand the drinking water’s quality. Remember that dissolved solids easily enter the water supply from various sources.
Here are the reasons why you should start measuring TDS:
1. Health
If the TDS levels are high, non-toxic substances, such as sodium, chloride, and potassium, are present in the water. However, other toxic ions are also present, including nitrate, cadmium, and arsenic.
2. Water Hardness
If the TDS level is high, it also indicates hard water. Beware that hard water causes weak performance of pipes and valves, sediment buildup, and additional maintenance costs.

3. Filter Efficiency
When you test TDS in water, knowing if your filter is working efficiently or not is a lot easier. Then, you also have an idea if it’s time to replace your filters.
4. Water Taste
Small TDS amounts help improve the water taste. However, too many TDS present in water gives the water you drink a metallic, bitter, or salty taste. That is why many people prefer drinking diet soda over water.
5. Cooking
High TDS levels do affect not only the taste of water but also the food’s taste.
6. Cleaning
If you use water with high TDS levels to clean your utensils, you will notice some ugly spots. High TDS levels can also fade the colors of the clothes and leave sediment buildup in the faucets, tubs, and sinks.
Below is a table about the TDS in water’s permissible range:
| TDS Levels in Milligram per Liter (mg/L) | Remarks |
| Less than 50 mg/L | Unacceptable due to lack of essential minerals |
| 50 to 150 mg/L | Acceptable for drinking |
| 150 to 250 mg/L | The water is excellent for individuals suffering from cardiovascular diseases |
| 250 to 350 mg/L | The water is excellent for individuals suffering from cardiovascular diseases |
| 350 to 500 mg/L | Fairly acceptable |
| 500 to 900 | Less acceptable |
| 1200 to 2000 | Not acceptable for drinking |
| Above 2000 | Not acceptable for drinking |
Below is a table about the TDS level palatable quotient:
| TDS Level in Parts Per Million (PPM) | Palatable Quotient |
| Above 1200 | Unacceptable |
| 300 to 500 | Poor |
| 250 to 300 | Fair |
| 150 to 250 | Good |
| 50 to 150 | Excellent for Drinking |
Now let’s see some examples of high and low TDS water sources.
Examples of High and Low TDS Water Sources
If water like rainwater or iceberg water has not undergone natural draining through the ground, the TDS levels are typically lower than the water sourced from artesian wells or springs. It occurs because of the following factors:
- Mineral abundance in the geological strata
- The easiness the minerals can dissolve into the water
- The period the water is in contact with a geological mineral source
To help you get a big picture of the TDS water sources, check out the tables below:
| TDS Level | Rating |
| 0 to 50 mg/L | Super Low |
| 50 to 250 mg/L | Low |
| 250 to 800 mg/L | Medium |
| 800 to 1500 mg/L | High |
| Over 1500 mg/L | Very High |
High TDS Level Water Sources
| Water Source | TDS Level |
| Spring | 7400 mg/L |
| Hot spring | 3052 mg/L |
| Volcanic spring | 2527 mg/L |
Low TDS Level Water Sources
| Water Source | TDS Level |
| Rainwater | 45 mg/L |
| Iceberg | 21 mg/L |
| Granite Strata Spring | 4 mg/L |
Does a High TDS Meter Reading Means You Need a Water Filter?
High TDS levels can produce hard water, leaving films and deposits on fixtures inside boilers and hot water pipes. They also indicate harmful contaminants, such as bromide, arsenic, manganese, sulfate, and iron.
While you can use a water filter to get rid of those contaminants, your filtration system may not correctly filter TDS.
How to Reduce TDS in Water?
If you test the water and the result is a high TDS level, you may wonder how to reduce it. Don’t worry; below are several ways how you can reduce TDS in water:
1. Distillation
Distillation is where you need to boil water to produce vapor. As the water boils, steam is produced, rising to a cool surface. Then, it will condense back into its liquid form.
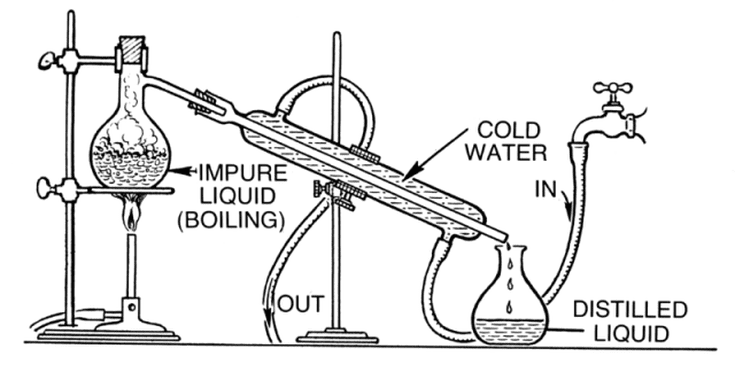
In this process, the dissolved salts cannot vaporize, so they stay in the boiling solution.
2. Deionization (DI)
Deionization involved passing through water in the positive and negative electrodes. With the ion-selective membranes, positive ions are separated from the water. Then, they move toward the negative methods.
As a result, de-ionized water is produced with high purity. On the other hand, water is initially passed through the RO unit to eliminate non-ionic organic contaminants.
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
This process eliminates TDS since water is forced through the synthetic membrane. Beware that this membrane contains microscopic pores, enabling only less than 0.0001 microns to pass through.
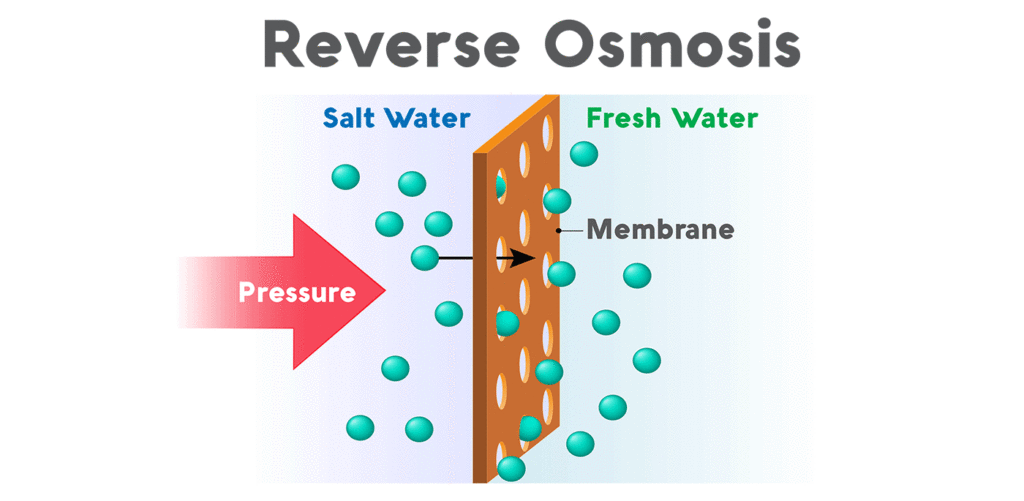
When the dissolved salts and metals’ molecules tend to be large compared to water, salts and metals are left behind after water is squeezed through the membrane.
Final Thoughts
Even if the water is high in TDS, it does not necessarily mean it is unsafe to drink. Sometimes, it indicates that the water is odd in smell, color, or taste.
Fortunately, you can test the TDS in water using a TDS meter and ensure that the water you drink suits your needs.
If the TDS level is high, you can try different methods to reduce it, such as reverse osmosis, distillation, and deionization.
FAQ
Why do we measure TDS in water?
Testing the water TDS levels helps check the water’s quality for different purposes. It is critical to measure TDS in water to understand better the taste, health purposes, filter maintenance needs, and cleaning and cooking purposes. It also helps you determine if chlorides, sodium, potassium, and toxic ions like arsenic, cadmium, and nitrate are present in water.
What is a good TDS level for drinking water?
If the TDS level is between 150-250, then it is suitable for drinking. Then, if it is between 50-150, that level is excellent for drinking.
What are the reasons to constantly monitor TDS?
Constant monitoring of TDS levels is critical to ensure that the membranes or filters effectively remove bacteria and impurities from the water. It also helps determine the filter performance, hardness of water, and other water qualities and purposes.
What does a TDS meter tell you?
This small hand-held device tells you the TDS in a solution, often water. A basic TDS meter measures the TDS amount in a solution. If you use advanced water, you can also check the temperature, salinity, and more.
